What Is A Solar Water Heater?
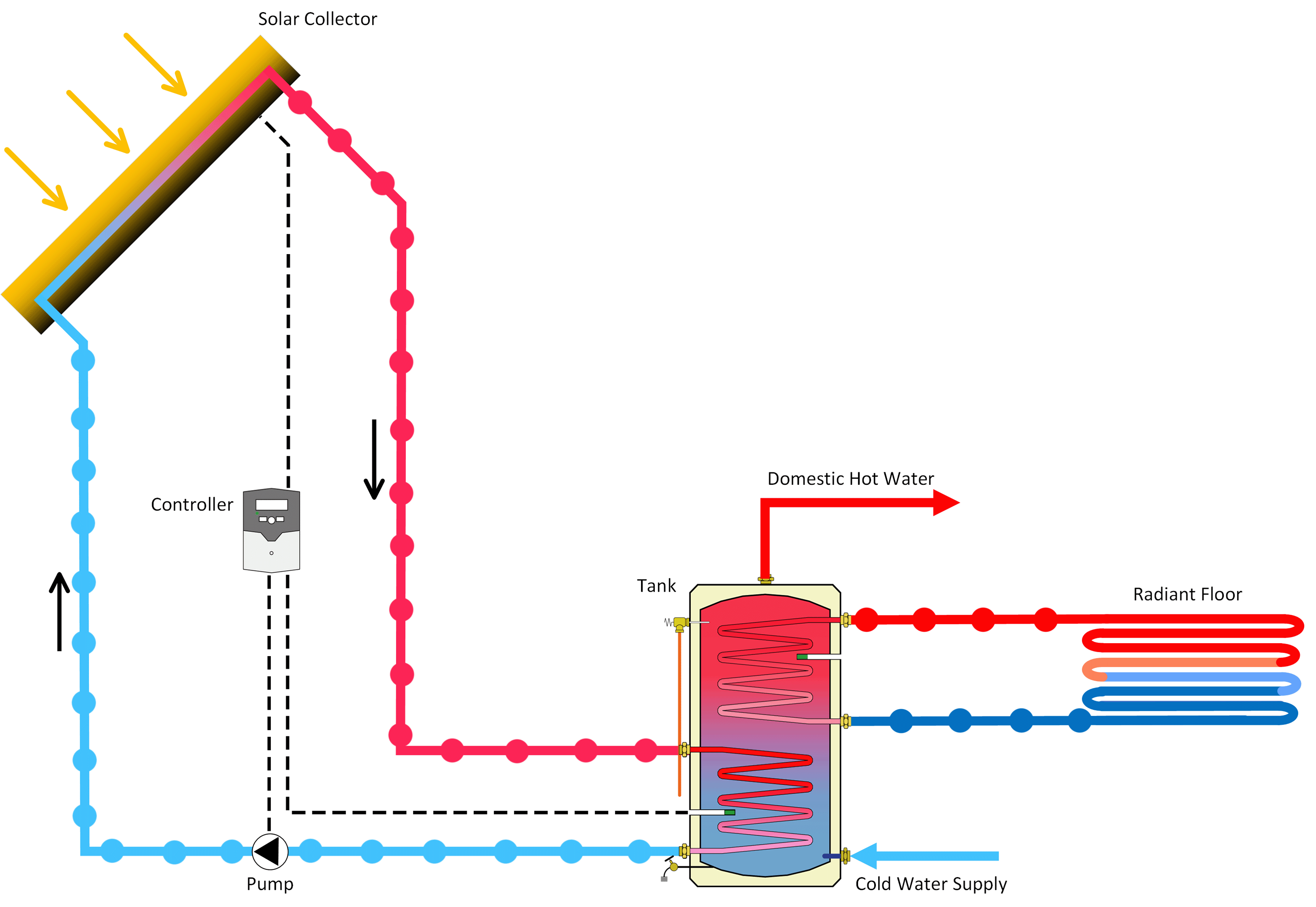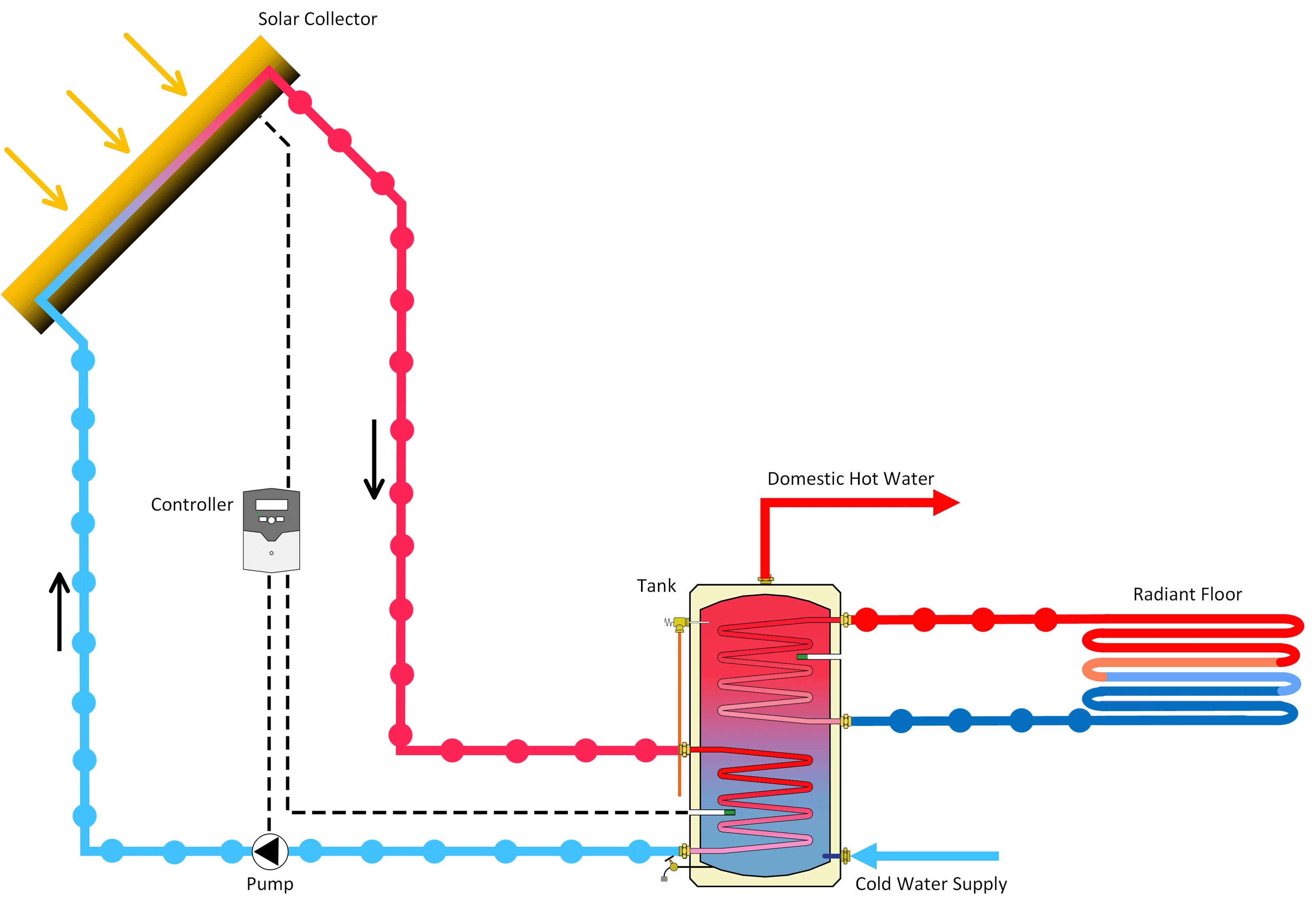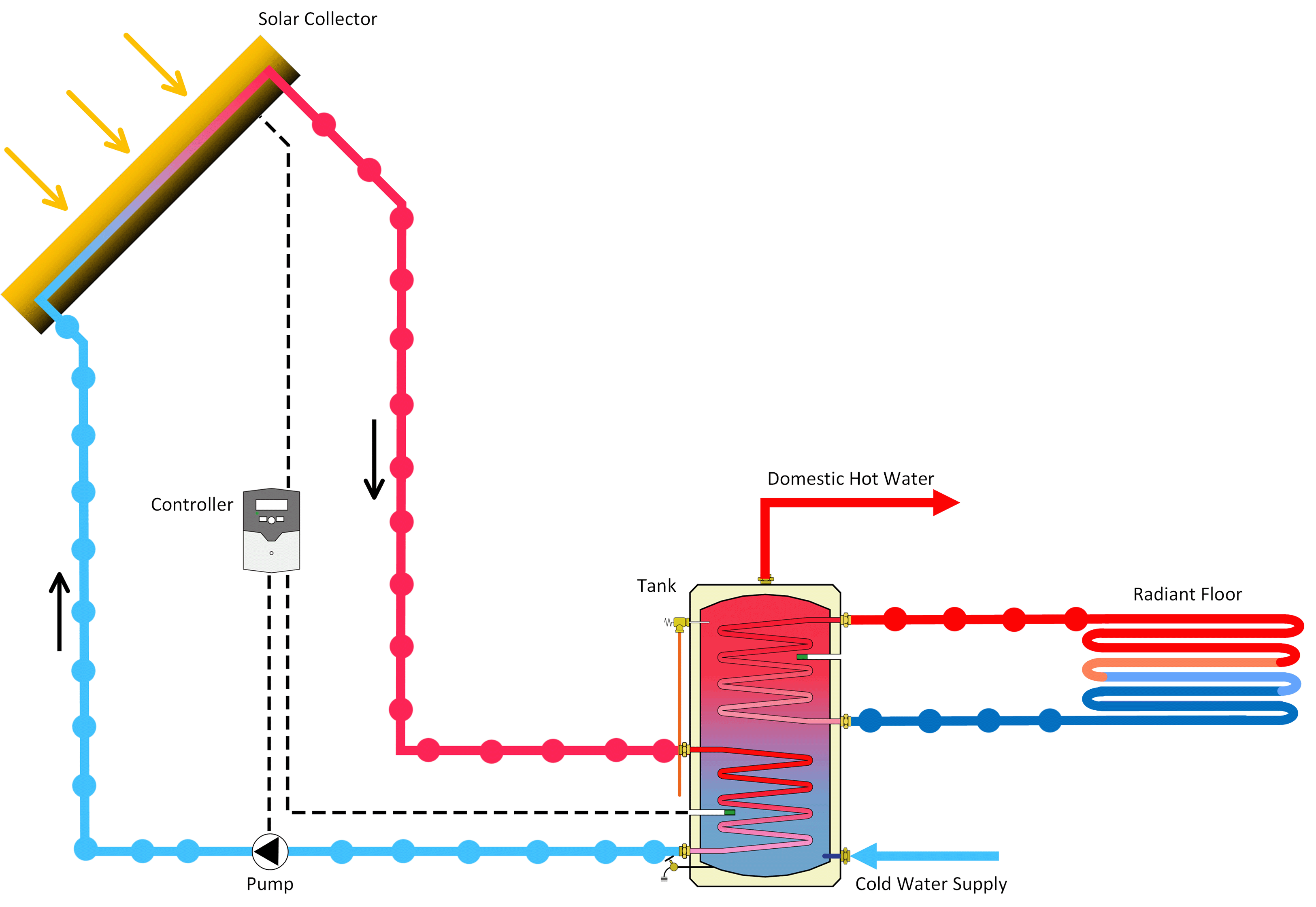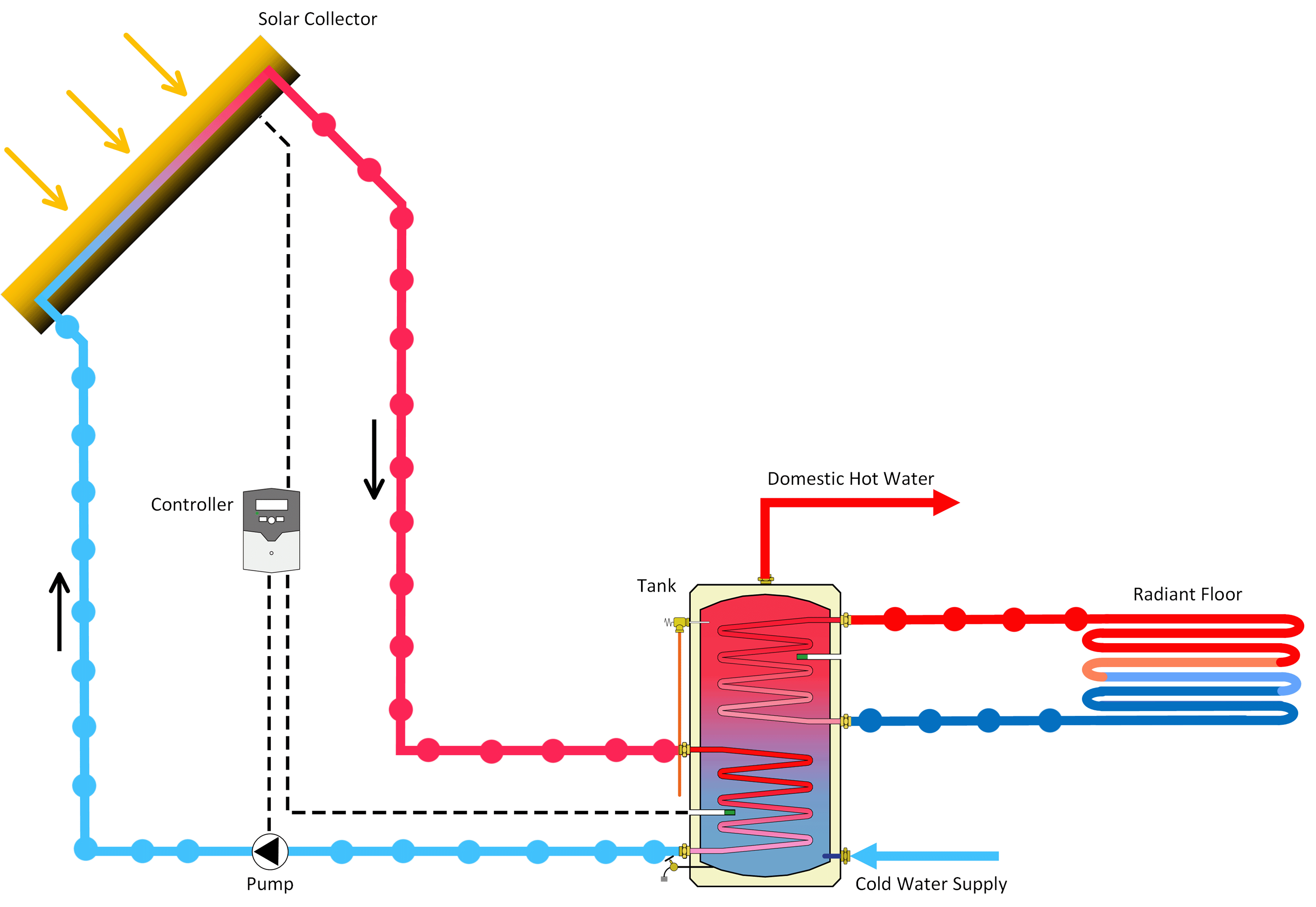
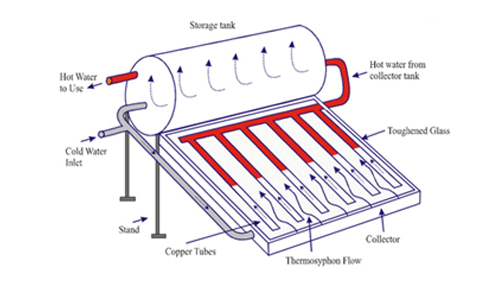
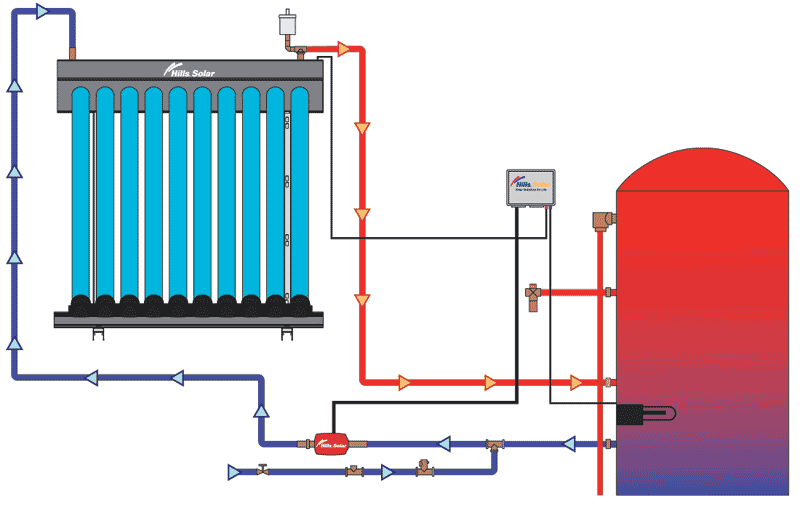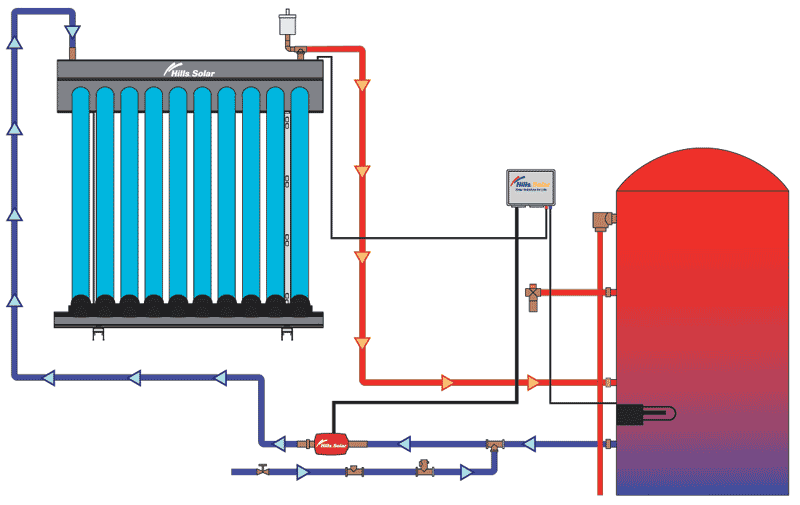
A solar water heater is a system that heats water using energy from the sun. It typically consists of a solar collector and a water storage tank, usually installed on the rooftop of a building to maximize exposure to sunlight.
There are two main ways the system can heat water:
- Direct Circulation – Cold water from the tank flows through the solar collector, gets heated by solar energy, and returns to the tank.
- Indirect Circulation – A heat-transfer fluid is heated in the collector and then passes through a heat exchanger, transferring its heat to the water in the storage tank.
Solar water heaters are classified into two types:
- Active Systems: These use pumps, valves, and controllers to circulate the fluid and manage the heating process.
- Passive Systems: These rely on natural convection and gravity to move water or heat without any mechanical components.
Solar water heaters are energy-efficient, eco-friendly, and help reduce electricity or fuel costs, making them a sustainable choice for residential and commercial hot water needs.